Sentence Diagramming (Easy Rules and Examples)

Sentence Diagramming is the best way to get a deeper understanding of the grammatical structure of a sentence. It helps in learning how each component in a sentence works together. Practicing sentence diagramming enables the creation of simple and complex sentences with ease. Below is a detailed explanation of what sentence diagramming is with examples.
What Is Sentence Diagramming?
A sentence contains different components that work together. The sentence diagramming helps in understanding how each component works in the sentence. To put it in simple words, it helps in understanding what role each word in the sentence plays and how the words work together.
After writing a sentence, if it feels something is wrong with the sentence, try diagramming. Breaking the components of a sentence into a pictorial representation will help in clearing out all the apprehensions regarding the sentence. Through this practice, sentences are clearly formed with free of grammatical errors.
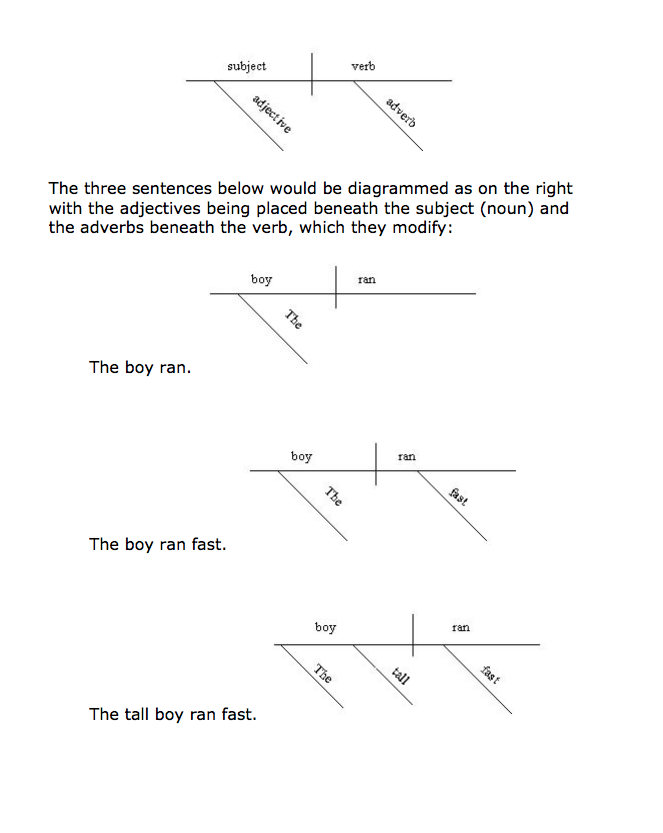
Here is a list of a few basic components or parts of a sentence:
Understanding Sentence Diagramming
To get a hang of sentence diagramming, it is important to understand each of the components in the sentence. Here is a brief overview of each of the components in a sentence.
Simple Subject And Predicate
Every sentence contains a subject and a predicate. A subject refers to what or who the sentence is about and the predicate speaks about the action done by the subject. In sentence diagramming, a horizontal line is drawn to represent the subject and predicate and a vertical line is drawn in between to separate them.
Examples
- Ross caught the ball. Here “Ross” is the subject and “caught the ball ” is the predicate. Both “Ross” and “caught the ball” should be represented on a horizontal line and a vertical line should be drawn between them. The subject should be written on the left side of the horizontal line and the predicate on the right.
- Amelie eats vegetables. Here “Amelie” is the subject and “eats vegetables” is the predicate. Both “Amelie” and “eats vegetables” should be represented on a horizontal line and a vertical line should be drawn between them.
Understood Subject
To understand this, let’s look at an example.
Learn your subjects thoroughly.
In the above example, there is no subject mentioned. Here the subject is “you”. The sentence is literally saying that “you need to learn your subjects thoroughly”. In sentences, sometimes the subject is not stated rather it should be understood by the reader. This is known as an understood subject.
In sentence diagramming, the understood subject is represented in parenthesis in the subject place.
Examples
- Close the front door. Here, the understood subject is “you”. In sentence diagramming, it should be represented as .
- Call your father at this moment. Here also the understood subject is “you”.
Questions
A sentence that asks a question is what an interrogative sentence is. Its structure is different from the typical declarative sentence.
In sentence diagramming, the subject and predicate of the interrogative sentence are written on the left side of the horizontal line and the right side of the horizontal line respectively. Between them, a vertical line is drawn.
Examples
- Is Tom coming? Here, “Tom” is the subject, and “Is coming” is the predicate.
- Are the siblings eating right now? Here, “siblings” is the subject, and “Are resting right now” is the predicate.
Compound Predicate
A compound predicate refers to a subject performing two actions in a sentence.
Examples
- The teacher taught math and gave homework. Here “teacher” is the subject. “Taught” and “gave” is the compound predicate.
- I went to the market and bought vegetables. Here, “I” is the subject. “Went” and “bought” is the compound predicate.
Compound Subject
A sentence with more than one subject is a compound subject.
Examples
- Tom and Amelie are reading books. Here “Tom” and “Amelie” are two subjects.
- Ross and Donald ran the marathon yesterday. Here “Ross” and “Donald” are the subjects.
Three Subjects
A sentence with three subjects is a “three subjects” sentence.
Examples
- Ross, Amelie, and Tom are writing. Here “Tom”, “Amelie”, and “Ross” are three subjects.
- The dog, cat, and goat are sitting side by side. Here “dog”, “cat”, and “goat” are three subjects.
Direct Object
It is a noun that receives the action of a verb. Let’s look at this with an example.
The boy kicked the ball. Here “boy” is the subject, “kicked” is the verb, and “ball” is the object. In this example “ball” is direct object.
Examples
- She went to the market. Here “market” is direct object.
- He plays football. Here “football” is direct object.
The Compound Direct Objects
When more than one noun or group of words acting as a noun receive the action of the same verb, it is the compound direct objects
Examples
- I visited America and Canada. Here “I” is the subject, “visited” is the verb, and “America” and “Canada” are direct compound objects.
- Tom ate chocolates and cookies. Here “Tom” is the subject, and “chocolates” and “cookies” are the compound direct objects. “Ate” is the verb.
Three Direct Objects
A sentence with three objects is a “three direct objects” sentence. Here, the subject performs an action with three objects.
Examples
- Tom sent a postcard, an email, and flowers to his friend. Here the subject is sending three objects to his friends which are “postcard”, “email”, and “flowers”.
- Amelie ate a banana, cake, and chips for tea. Here “banana”, “cake”, and “chips” are three objects.
The Compound Predicate With Direct Objects
It means a subject is performing more than one action with more than one object.
Examples
- Tom cooked the chicken and vegetables and ate them. Here “Tom” is the subject. “Cooked the chicken and vegetables and ate them” is a compound predicate with two verbs “cooked” and “ate”. It also contains two objects ”chicken” and “vegetables”.
- My mother washed my shirt and jeans and put them on the clothesline. Here “mother” is the subject. “Washed my shirt and jeans and put them on the clothesline” is the compound predicate.
Compound Predicate With One Direct Object
This means a subject is performing two actions (verbs) with one object.
Examples
- Shawn writes and sings his songs. Here the subject is “Shawn”. “Writes and sings his songs” is a compound predicate that contains two verbs, “writes” and “sings” and a direct object “songs”.
- He chops and cooks the vegetables. The subject is “he”. “Chops and cooks the vegetables” is a compound predicate.
The Indirect Object
It is optional in the sentence and it is the recipient of an action.
Examples
- The teacher gave me a book. The subject is “teacher”. “Me” is the indirect object.
- I gave her some clothes. The subject is “I”. “Her” is the indirect object.
The Compound Indirect Objects
This means more than one indirect object is the recipient of an action.
Examples
- My father gave Tom and Amelie are ride to school. The subject is “father”. “Tom” and “Amelie” are compound indirect objects.
- She gave my friend and me a book to study. The subject is “she”. “friend” and “me” are the compound indirect objects.
Predicate Noun
A predicate noun is a noun that comes after a linking verb and gives extra information about the subject.
Examples
- Mrs. Richardson is the acting principal of the school. The subject is “Richardson”. The linking verb is “is”. “Acting principal” is the noun predicate.
- I am the class monitor. The subject is “I”. The linking verb is “am”. “Class monitor” is the noun predicate.
Objective Complement
An objective complement is a noun or adjective that comes after a direct object that changes the state of the object or renames it.
Examples
- Spicy food makes Shawn angry. Here “Shawn” is direct object and “angry” is the objective complement.
- Pop music makes me happy. Here “me” is direct object and “happy” is the objective complement.
Reflexive Pronouns
It refers back to a person or thing in the same sentence. Words like myself, yourself, and himself are reflexive pronouns.
Examples
- I was getting late, so I drove the car myself. Here “myself” is a reflexive pronoun.
- Annie does all the chores herself because she hasa lot of time. Here “herself” is a reflexive pronoun.
Intensive Pronoun
Intensive pronoun puts force on the statement. It ends in “self” or “selves” like “yourselves”, “myself”, and “ourselves”.
Examples
- We cooked all the food ourselves.
- I have done all the washing myself.
Appositive
An appositive is a noun or pronoun that explains another noun or pronoun that is beside it.
Examples
- Your brother Tom is in trouble. Here “brother” is a noun and “Tom” is the appositive.
- Your sister Amy is in town. Here “sister” is a noun and “Amy” is the appositive.
Interjection
An interject is a short word that expresses emotion like “Oh!” and “Wow!”.
Examples
- Ouch! I hurt myself.
- Wow! That is a beautiful landscape.
Adjective
A word that describes a noun or pronoun.
Examples
- This is a beautiful painting. “Beautiful” is the adjective.
- This shop is big. “Big” is the adjective.
Compound Adjectives
When two or more adjectives are joined together to modify the same noun, it is called a compound adjective.
Examples
- This is a six-foot (compound adjective) bed.
- I got a white-collar (compound adjective) job.
Predicate Adjective
A predicate adjective describes the subject in a sentence. It follows a linking verb.
Examples
- His music sounds soothing. Here “music” is the subject, “sounds” is the linking verb, and “soothing” is a predicate adjective.
- Her dance recital was amazing. Here “dance recital” is the subject, “was” is the linking verb, and “amazing” is a predicate adjective.
Compound Predicate Adjective
When there is more than one predicate adjective that modifies the same noun it is known as a compound predicate adjective.
Examples
- These doughnuts are cold and hard. “Cold” and “hard‘ are compound predicate adjective.
- The actress is tall, beautiful, and smart. “Tall”, “beautiful”, and “smart” are compound predicative adjective.
Comparative Adjective
It is used for comparing two nouns. Words like taller and smarter are used.
Examples
- Tom runs faster than John. “Faster” is the comparative adjective.
- My house is smaller than Jill’s house. “Smaller” is the comparative adjective.
Adverb
It is a word that describes a verb, an adjective, or a complete sentence.
Examples
- She walks slowly. “Slowly” is the adverb.
- He reached the hospital quickly. “Quickly” is the adverb.
Adverbs Modifying Other Adverbs
It provides extra information about the adverb by using another one before it.
Examples
- My grandmother walks very slowly. “Very” is the adverb used to describe the other adverb “slowly”.
- She walked very quickly to the bus stop.
Compound Adverbs
A compound adverb is combined with another noun, adverb, adjective, or verb.
Examples
- The mechanic detected early on that the car’s engine had failed. “Early on” is a compound adverb.
- He introduced himself in a self-conscious way. “Self-conscious” is a compound adverb.
Prepositional Phrase
It is a phrase consisting of a preposition, a noun, and modifiers.
Examples
- The girl sat on her chair. Here “on” is the preposition, “chair” is the object of the preposition, and “her” is the modifier.
- He lives in her apartment. Here “in” is the preposition, “apartment” is the object of the preposition, and “her” is the modifier.
The Prepositional Phrase Modifies Another Prepositional Phrase
Examples
- He is walking on the sand by the sea. Here “on the sand” and “by the sea” are two propositional phrases.
The Preposition Along With Compound Objects
When two or more objects follow a preposition then it is called a preposition with compound objects.
Examples
- Tomorrow I am going to a movie, a restaurant, and a beauty parlor. Here “to” is the preposition followed by “movie”, “restaurant”, and “beauty parlor” which are compound objects of the preposition “to”.
- John always thinks about (preposition) hockey players and baseball players. “Hockey players and baseball players” are compound objects of the preposition “about”.
Prepositional Phrase Modifies An Adverb
When a prepositional phrase acts on a verb then it is said to be a propositional phrase modifying an adverb.
Examples
- The cat jumped up with excitement.
The Prepositional Phrase As A Subjective Complement
In English grammar, preposition phrase functions as a subject complement. Here are the examples.
Examples
- My best part of the workday is during the evening. Here “during the evening” is the subject complement.
- The best place to read is in the reading room. Here “in the reading room” is the subject complement.
Participle
A participle is a kind of verb that describes a past or a present progressive action and is used as an adjective also.
Examples
- He is reading a book. “Reading” is a present participle.
- The vegetables were cooked in the oven. “Were cooked” past participle.
Participial Phrase
It consists of a participle along with other words that add information to the noun or pronoun.
Examples
- Holding (present participle) the father’s hand nervously, the child approached the principal.
Gerund
A gerund is a verb that is in the “-ing” form and acts as a noun.
Examples
- Reading is one of my favorite hobbies. “Reading” is a gerund.
- Swimming is one of my routine exercises. “Swimming” is gerund.
Gerund Phrase As Object Of A Preposition
When a gerund phrase follows a preposition, then it is an object of the preposition. Here is an example.
Examples
- Tom’s interest in studying Biology improved. Here “studying” is a gerund. “Studying Biology” is the gerund phrase. Gerund phrase acts as the object of the preposition “in”.
Infinitive As A Noun
An infinitive is a kind of verb that acts as a noun, adverb, or adjective. It is made of two words that are – to + verb. Below are examples of an infinitive as a noun.
Examples
- To dance is my favorite hobby. “To+dance” (noun).
- To walk on the beach is my daily routine. “To+walk” (noun).
The Infinitive Acting As An Adjective
Below are examples of an infinitive acting as an adjective.
Examples
- Spiderman is the movie to watch. “To+watch” (adjective).
- Elders are the people to care. “To+care” (adjective).
The Infinitive Acting As An Adverb
Below are examples of an infinitive acting as an adverb.
Examples
- It is difficult to play in the rain. “To+play” (adverb).
- It is easy to make an omelet. “To+make” (adverb).
The Infinitive As Direct Object
Below are examples of an infinitive as a direct object.
Examples
- He likes to solve puzzles. “To+solve” (infinitive verb) and “puzzles” is direct object.
- He loves to read novels. “To+read” (infinitive verb) and “novels” is direct object.
Causative Verb
A causative verb is a verb that refers to a person or thing that makes something happen. Make, help, and allow are some causative verbs.
Examples
- He had (causative verb) John do the work.
- My mother always makes (causative verb) me clean the room.
Expletive Construction
They are phrases or sentences that start with words like “there are” and “It is”.
Examples
- It is going to be a long tedious journey.
- There are going to be participants at the conference.
Absolute Construction
It is a group of words at the start of the sentence that has no connection grammatically with the rest of the sentence.
Examples
- To be frank, I don’t know when I met him.
- To be truthful, I did not cook this meal.
Correlative Conjunction
They are conjunctions that explain how two words or phrases relate to each other in a sentence.
Examples
- I will buy shoes either at Adidas or at Nike.
- I will neither drink tea nor coffee.
Passive Verbs
A passive verb is used when the subject does not perform the action but receives the action.
Examples
- The window was broken by the children.
- This book was written by Shakespeare.
Sources
- Everything You Need to Know About Sentence Diagramming
- How To Diagram A Sentence
- Learn How to Diagram a Sentence
- Sentence Diagramming Worksheets: Compound Predicates
- Diagramming Sentences Exercises: Chapter 1
Inside this article

Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.







